Agenda¶
- Numpy
- Introduction
- N-dimensional ndarray
- Create ndarray
- Inspect
- Reshaping
- Mathematics
- Pandas
- Introduction
- Structure
- Reading Files
- Inspect
- Descriptive Statistics
- Matplotlib
- Introduction
- Basic
- Plots
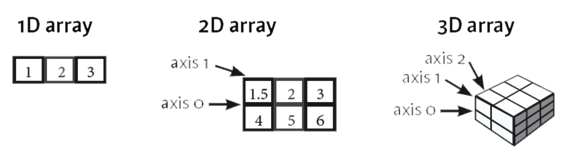
Numpy¶
import numpy as np
array_1d = np.array( [1,2,3] )
print('array_1d 的資料型態',type(array_1d))
print(array_1d)
array_1d 的資料型態 <class 'numpy.ndarray'> [1 2 3]
array_2d = np.array( [ [1,2,3],
[4,5,6],
[7,8,9] ])
print('array_2d 的資料型態',type(array_2d))
print(array_2d)
array_2d 的資料型態 <class 'numpy.ndarray'> [[1 2 3] [4 5 6] [7 8 9]]
Numpy¶
Create ndarray¶
- np.array(x) : 基本建立
- np.zeros(x) : x 是維度 ( 建立一個由 0 組成的 ndarray )
- np.ones(x) : x 是維度 ( 建立一個由 1 組成的 ndarray )
- np.empty(x) : x 是維度 ( 建立一個空的 ndarray )
- np.arange(start, stop, step) : 似 range()
- np.random.random(x) : x 是維度 (隨機產生0~1的值並組成ndarray)
- np.random.uniform(low, high, n) : 隨機產生 n 個介在 low~high 的值並服從 unifom
- np.random.normal(mu, sigma, n) : 隨機產生 n 個服從 normal( $\mu$ , $\sigma$ ) )
Exercise 希望將 Temperature_Taipei 中的所有溫度都轉成華氏
Temperature_Taipei = [22, 24, 19, 19, 30, 21, 25]
公式: $Fahrenheit = Celsius × (9/5) + 32$
Temperature_Taipei = [22, 24, 19, 19, 30, 21, 25]
print( list( map( lambda i : i * (9/5)+32, Temperature_Taipei ) ) )
[71.6, 75.2, 66.2, 66.2, 86.0, 69.80000000000001, 77.0]
Temperature_array = np.array( [22, 24, 19, 19, 30, 21, 25] )
Note 將 list 轉為 ndarray
Temperature_array = np.array( Temperature_Taipei )
Temperature_array_Fahrenheit = (Temperature_array)*(9/5)+32
print(Temperature_array_Fahrenheit)
[71.6 75.2 66.2 66.2 86. 69.8 77. ]
print( np.zeros( (2,3) ) )
[[0. 0. 0.] [0. 0. 0.]]
Note ( 2 ,3 ) :表示一個 2 列 3 行二維的陣列
print( np.ones( (2,3,4) ) )
[[[1. 1. 1. 1.] [1. 1. 1. 1.] [1. 1. 1. 1.]] [[1. 1. 1. 1.] [1. 1. 1. 1.] [1. 1. 1. 1.]]]
Note ( 2 ,3 ,4 ) :表示一個 2 頁 3 列 4 行的三維陣列
print( np.empty( (2,2) ) )
[[-1.72723371e-077 3.11109624e+231] [ 2.00390337e+000 2.82476877e-309]]
Note 陣列中的元素為一個初始化值
multiplication = np.empty( (9 , 9) )
for i in range(1,10):
for j in range(1,10):
multiplication[(i-1),(j-1)]= i*j
print(multiplication)
[[ 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9.] [ 2. 4. 6. 8. 10. 12. 14. 16. 18.] [ 3. 6. 9. 12. 15. 18. 21. 24. 27.] [ 4. 8. 12. 16. 20. 24. 28. 32. 36.] [ 5. 10. 15. 20. 25. 30. 35. 40. 45.] [ 6. 12. 18. 24. 30. 36. 42. 48. 54.] [ 7. 14. 21. 28. 35. 42. 49. 56. 63.] [ 8. 16. 24. 32. 40. 48. 56. 64. 72.] [ 9. 18. 27. 36. 45. 54. 63. 72. 81.]]
print( np.arange(0,10,2) )
[0 2 4 6 8]
Review
print( list(range(0,10,2)) )
[0, 2, 4, 6, 8]
隨機產生 0~1 的數值
print( np.random.random( (2,3) ) )
[[0.10322868 0.00594036 0.71135141] [0.76162664 0.5414609 0.14193007]]
隨機產生 0~10 的數值
print( np.random.random( (2,3) ) *10 )
[[3.57881303 2.03389965 5.91201318] [5.67424712 2.89686344 7.88636533]]

unifom_distrbution = np.random.uniform(-1,1,25)
print(unifom_distrbution)
[ 0.71026914 -0.61457316 0.18452574 -0.31136488 0.99949133 -0.30695047 0.5594765 0.04748817 -0.3808115 -0.27115919 -0.49922516 -0.53045431 -0.87853298 0.43181305 -0.31889286 0.03479911 0.36622747 0.32436697 0.12805869 -0.91375168 0.60443956 0.91088484 0.62479195 0.06079643 -0.60145948]
Note 設定 seed 可以固定每次 random 產生的結果
np.random.seed(100)
unifom_distrbution = np.random.uniform(-1,1,25)
print(unifom_distrbution)
[ 0.08680988 -0.44326123 -0.15096482 0.68955226 -0.99056229 -0.75686176 0.34149817 0.65170551 -0.72658682 0.15018666 0.78264391 -0.58159576 -0.62934356 -0.78324622 -0.56060501 0.95724757 0.6233663 -0.65611797 0.6324495 -0.45185251 -0.13659163 0.88005964 0.63529876 -0.3277761 -0.64917909]

normal_distrbution = np.random.normal( 0 , 1 , 20 )
print(normal_distrbution)
[ 0.78148842 -0.65438103 0.04117247 -0.20191691 -0.87081315 0.22893207 -0.40803994 -0.10392514 1.56717879 0.49702472 1.15587233 1.83861168 1.53572662 0.25499773 -0.84415725 -0.98294346 -0.30609783 0.83850061 -1.69084816 1.15117366]
Note 設定 seed 可以固定每次 random 產生的結果
np.random.seed(100)
normal_distrbution = np.random.normal( 0 , 1 , 20 )
print(normal_distrbution)
[-1.74976547 0.3426804 1.1530358 -0.25243604 0.98132079 0.51421884 0.22117967 -1.07004333 -0.18949583 0.25500144 -0.45802699 0.43516349 -0.58359505 0.81684707 0.67272081 -0.10441114 -0.53128038 1.02973269 -0.43813562 -1.11831825]
Exercise 確認 array_2d 中元素個數
print( array_2d.size )
9
Review len
my_list = [0, 2, 4, 6, 8]
print( len(my_list) )
5
Exercise 確認 array_2d 中矩陣的外觀
print( array_2d.shape )
(3, 3)
Exercise 確認 array_2d 的維度
print( array_2d.ndim )
2
Exercise 檢查 array_2d 中元素的型態
print( array_2d.dtype )
int64
x_int = np.array([1 ,2 ,3] ,dtype=np.int) #利用 dtype 定義一個 int 的 ndarray
print(x_int)
[1 2 3]
print( "x_int 的資料型態", type(x_int) )
print( "---------------------------------" )
print( "x_int 元素的資料型態", x_int.dtype )
x_int 的資料型態 <class 'numpy.ndarray'> --------------------------------- x_int 元素的資料型態 int64
Note
- 默認是 64 位元的 int,也有 16, 32 位元
- 位元越小佔用的空間越小,若想要精確就必須用大一點。
x_float= np.array([1 ,2 ,3] ,dtype=np.float) #利用 dtype 定義一個 float 的 ndarray
print(x_float)
[1. 2. 3.]
print( "x_float 的資料型態", type(x_float) )
print( "---------------------------------" )
print( "x_float 元素的資料型態", x_float.dtype )
x_float 的資料型態 <class 'numpy.ndarray'> --------------------------------- x_float 元素的資料型態 float64
x_str = np.array([1 ,2 ,3] ,dtype=np.str) #利用 dtype 定義一個 str 的 ndarray
print(x_str)
['1' '2' '3']
print( "x_str 的資料型態", type(x_str) )
print( "---------------------------------" )
print( "x_str 元素的資料型態", x_str.dtype )
x_str 的資料型態 <class 'numpy.ndarray'> --------------------------------- x_str 元素的資料型態 <U1
weather_array = np.array([ 'Taipei' , 18.5 , 'rainy' ])
print(weather_array)
print( "---------------------------------" )
print( "weather_array 元素的資料型態", weather_array.dtype )
['Taipei' '18.5' 'rainy'] --------------------------------- weather_array 元素的資料型態 <U6
Exercise 隨機生成 一個名為 normal_random (20×1) 的ndarray,服從 normal(0,1)
normal_random = np.random.normal(0,1,20)
print(normal_random)
print( "---------------------------------" )
print( "normal_random 的維度", normal_random.ndim )
print( "---------------------------------" )
print( "normal_random 的外觀", normal_random.shape )
[ 1.61898166 1.54160517 -0.25187914 -0.84243574 0.18451869 0.9370822 0.73100034 1.36155613 -0.32623806 0.05567601 0.22239961 -1.443217 -0.75635231 0.81645401 0.75044476 -0.45594693 1.18962227 -1.69061683 -1.35639905 -1.23243451] --------------------------------- normal_random 的維度 1 --------------------------------- normal_random 的外觀 (20,)
Exercise 利用 .reshape 將 normal_random 資料轉成 2d-ndarray(4X5)
normal_random_new = normal_random.reshape(4,5)
print(normal_random_new)
print( "---------------------------------" )
print( "normal_random_new 的外觀", normal_random_new.shape )
[[ 1.61898166 1.54160517 -0.25187914 -0.84243574 0.18451869] [ 0.9370822 0.73100034 1.36155613 -0.32623806 0.05567601] [ 0.22239961 -1.443217 -0.75635231 0.81645401 0.75044476] [-0.45594693 1.18962227 -1.69061683 -1.35639905 -1.23243451]] --------------------------------- normal_random_new 的外觀 (4, 5)
Exercise 將 array_2d 轉置
array_2d.T
array([[1, 4, 7],
[2, 5, 8],
[3, 6, 9]])
A = np.array([[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]])
print(A)
[[1 2 3] [4 5 6] [7 8 9]]
B = np.array([[1,1,1],[2,2,2],[3,3,3]])
print(B)
[[1 1 1] [2 2 2] [3 3 3]]
Exercise 將 A 乘上一個常數
A * 2
array([[ 2, 4, 6],
[ 8, 10, 12],
[14, 16, 18]])
Exercise 將 A , B 兩矩陣元素相乘
A * B
array([[ 1, 2, 3],
[ 8, 10, 12],
[21, 24, 27]])

Numpy¶
Mathematics¶
np.dot(A , B ): 兩ndarray相乘 (兩矩陣相乘)
source:http://www.stoimen.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2012/11/4.-Rect-Matrix-Multiplication.png
Exercise 將 A , B 兩矩陣相乘
np.dot(A , B )
array([[14, 14, 14],
[32, 32, 32],
[50, 50, 50]])

Numpy¶
Mathematics¶
np.min(x): 找出ndarray中最小值np.max(x): 找出ndarray中最大值
Example
print(normal_distrbution)
[-1.74976547 0.3426804 1.1530358 -0.25243604 0.98132079
0.51421884 0.22117967 -1.07004333 -0.18949583 0.25500144
-0.45802699 0.43516349 -0.58359505 0.81684707 0.67272081
-0.10441114 -0.53128038 1.02973269 -0.43813562 -1.11831825]Exercise 分別找出 normal_distrbution 中最大、最小值
print("normal_distrbution 的最小值:", np.min(normal_distrbution))
print("normal_distrbution 的最大值:", np.max(normal_distrbution))
normal_distrbution 的最小值: -1.7497654730546974 normal_distrbution 的最大值: 1.153035802563644
Exercise 分別找出 normal_distrbution 的總和、平均數、標準差、中位數
print("normal_distrbution 的總和:", np.sum(normal_distrbution))
print("normal_distrbution 的平均數:", np.mean(normal_distrbution))
print("normal_distrbution 的標準差:", np.std(normal_distrbution))
print("normal_distrbution 的中位數:", np.median(normal_distrbution))
normal_distrbution 的總和: -0.07360709761201556 normal_distrbution 的平均數: -0.003680354880600778 normal_distrbution 的標準差: 0.7664839465468608 normal_distrbution 的中位數: 0.05838426291538637
Pandas¶
import pandas as pd
Taipei_array = np.array([17.0,8.3,20.1,22.6,27.0,27.8,30.1,30.3,29.4,27.1,24.0,17.5,])
print("Taipei_array 的資料型態", type(Taipei_array))
print( "---------------------------------" )
print(Taipei_array)
Taipei_array 的資料型態 <class 'numpy.ndarray'> --------------------------------- [17. 8.3 20.1 22.6 27. 27.8 30.1 30.3 29.4 27.1 24. 17.5]
Taipei_series = pd.Series(Taipei_array)
print("Taipei_series 的資料型態", type(Taipei_series))
print( "---------------------------------" )
print(Taipei_series)
Taipei_series 的資料型態 <class 'pandas.core.series.Series'> --------------------------------- 0 17.0 1 8.3 2 20.1 3 22.6 4 27.0 5 27.8 6 30.1 7 30.3 8 29.4 9 27.1 10 24.0 11 17.5 dtype: float64
month = [ 'FEB', 'JAN', 'MAR', 'APR', 'MAY', 'JUN', 'JUL', 'AUG', 'SEP', 'OCT', 'NOV', 'DEC']
Taipei_series = pd.Series( Taipei_array ,
index = month )
print(Taipei_series)
FEB 17.0 JAN 8.3 MAR 20.1 APR 22.6 MAY 27.0 JUN 27.8 JUL 30.1 AUG 30.3 SEP 29.4 OCT 27.1 NOV 24.0 DEC 17.5 dtype: float64
print(Taipei_series['FEB'])
17.0
Taipei_dic = {'FEB': 17.0, 'JAN': 8.3, 'MAR': 20.1, 'APR': 22.6, 'MAY': 27.0, 'JUN': 27.8, 'JUL': 30.1, 'AUG': 30.3, 'SEP': 29.4, 'OCT': 27.1, 'NOV': 24.0, 'DEC': 17.5}
print("Taipei_dic 的資料型態", type(Taipei_dic))
print( "---------------------------------" )
print(Taipei_dic)
Taipei_dic 的資料型態 <class 'dict'>
---------------------------------
{'FEB': 17.0, 'JAN': 8.3, 'MAR': 20.1, 'APR': 22.6, 'MAY': 27.0, 'JUN': 27.8, 'JUL': 30.1, 'AUG': 30.3, 'SEP': 29.4, 'OCT': 27.1, 'NOV': 24.0, 'DEC': 17.5}
Note Dictionary 的 Key 會變成 index
Taipei_series = pd.Series(Taipei_dic)
print("Taipei_series 的資料型態", type(Taipei_series))
print( "---------------------------------" )
print(Taipei_series)
Taipei_series 的資料型態 <class 'pandas.core.series.Series'> --------------------------------- APR 22.6 AUG 30.3 DEC 17.5 FEB 17.0 JAN 8.3 JUL 30.1 JUN 27.8 MAR 20.1 MAY 27.0 NOV 24.0 OCT 27.1 SEP 29.4 dtype: float64
Temperature = np.array([[17.0,8.3,20.1,22.6,27.0,27.8,30.1,30.3,29.4,27.1,24.0,17.5],
[21.1,21.7,22.9,25.7,28.4,28.4,29.4,30.2,29.7,28.9,26.9,21.6]])
print("Temperature 的資料型態", type(Temperature))
print( "---------------------------------" )
print("Temperature 的外觀", np.shape(Temperature))
print( "---------------------------------" )
print(Temperature)
Temperature 的資料型態 <class 'numpy.ndarray'> --------------------------------- Temperature 的外觀 (2, 12) --------------------------------- [[17. 8.3 20.1 22.6 27. 27.8 30.1 30.3 29.4 27.1 24. 17.5] [21.1 21.7 22.9 25.7 28.4 28.4 29.4 30.2 29.7 28.9 26.9 21.6]]
Temperature_dataframe = pd.DataFrame(Temperature)
print("Temperature_dataframe 的資料型態", type(Temperature_dataframe))
print( "---------------------------------" )
print(Temperature_dataframe)
Temperature_dataframe 的資料型態 <class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
---------------------------------
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
0 17.0 8.3 20.1 22.6 27.0 27.8 30.1 30.3 29.4 27.1 24.0 17.5
1 21.1 21.7 22.9 25.7 28.4 28.4 29.4 30.2 29.7 28.9 26.9 21.6
Temperature_dataframe = pd.DataFrame(Temperature,
index=['Taipei','Kaohsiung'],
columns = month)
print(Temperature_dataframe)
FEB JAN MAR APR MAY JUN JUL AUG SEP OCT NOV \
Taipei 17.0 8.3 20.1 22.6 27.0 27.8 30.1 30.3 29.4 27.1 24.0
Kaohsiung 21.1 21.7 22.9 25.7 28.4 28.4 29.4 30.2 29.7 28.9 26.9
DEC
Taipei 17.5
Kaohsiung 21.6
Temperature_dic = {'FEB': [17.0,21.1], 'JAN': [8.3,21.7], 'MAR': [20.1,22.9], 'APR': [22.6,25.7], 'MAY': [27.0,28.4], 'JUN': [27.8,28.4],'JUL': [30.1,29.4], 'AUG': [30.3,30.2], 'SEP': [29.4,29.7], 'OCT': [27.1,28.9], 'NOV':[24.0,26.9], 'DEC': [17.5,21.6]}
print("Temperature_dic 的資料型態", type(Temperature_dic))
print( "---------------------------------" )
print(Temperature_dic)
Temperature_dic 的資料型態 <class 'dict'>
---------------------------------
{'FEB': [17.0, 21.1], 'JAN': [8.3, 21.7], 'MAR': [20.1, 22.9], 'APR': [22.6, 25.7], 'MAY': [27.0, 28.4], 'JUN': [27.8, 28.4], 'JUL': [30.1, 29.4], 'AUG': [30.3, 30.2], 'SEP': [29.4, 29.7], 'OCT': [27.1, 28.9], 'NOV': [24.0, 26.9], 'DEC': [17.5, 21.6]}
Note Dictionary 的 Key 會變成 column name
Temperature_dataframe = pd.DataFrame(Temperature_dic)
print("Temperature_dataframe 的資料型態", type(Temperature_dataframe))
print( "---------------------------------" )
print(Temperature_dataframe)
Temperature_dataframe 的資料型態 <class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
---------------------------------
APR AUG DEC FEB JAN JUL JUN MAR MAY NOV OCT SEP
0 22.6 30.3 17.5 17.0 8.3 30.1 27.8 20.1 27.0 24.0 27.1 29.4
1 25.7 30.2 21.6 21.1 21.7 29.4 28.4 22.9 28.4 26.9 28.9 29.7
Temperature_dataframe = pd.DataFrame(Temperature,
columns = month)
print(Temperature_dataframe)
FEB JAN MAR APR MAY JUN JUL AUG SEP OCT NOV DEC 0 17.0 8.3 20.1 22.6 27.0 27.8 30.1 30.3 29.4 27.1 24.0 17.5 1 21.1 21.7 22.9 25.7 28.4 28.4 29.4 30.2 29.7 28.9 26.9 21.6
Temperature_dataframe = pd.DataFrame(Temperature,
columns = month,
index=['Taipei','Kaohsiung'])
print(Temperature_dataframe)
FEB JAN MAR APR MAY JUN JUL AUG SEP OCT NOV \
Taipei 17.0 8.3 20.1 22.6 27.0 27.8 30.1 30.3 29.4 27.1 24.0
Kaohsiung 21.1 21.7 22.9 25.7 28.4 28.4 29.4 30.2 29.7 28.9 26.9
DEC
Taipei 17.5
Kaohsiung 21.6
Taipei = [17.0,8.3,20.1,22.6,27.0,27.8,30.1,30.3,29.4,27.1,24.0,17.5]
Kaohsiung = [21.1,21.7,22.9,25.7,28.4,28.4,29.4,30.2,29.7,28.9,26.9,21.6]
Quality = ['Good','Good','Bad','Bad','Bad','Good','Bad','Bad','Good','Bad','Good','Good']
Temperature = { 'Taipei' : Taipei ,
'Kaohsiung' : Kaohsiung ,
'Quality' : Quality }
Temperature_dataframe = pd.DataFrame(Temperature, index = month)
print(Temperature_dataframe)
Kaohsiung Quality Taipei FEB 21.1 Good 17.0 JAN 21.7 Good 8.3 MAR 22.9 Bad 20.1 APR 25.7 Bad 22.6 MAY 28.4 Bad 27.0 JUN 28.4 Good 27.8 JUL 29.4 Bad 30.1 AUG 30.2 Bad 30.3 SEP 29.7 Good 29.4 OCT 28.9 Bad 27.1 NOV 26.9 Good 24.0 DEC 21.6 Good 17.5
import os
os.getcwd()
'/Users/hsinyuchan/Desktop/TKUXPython'
Pandas¶
Reading Files¶
.read_csv( ): 讀取 csv 格式資料
2002 - 2016 年國民出國目的地人數統計
source:政府開放資料 http://data.gov.tw/node/7325
Aboard = pd.read_csv('/Users/hsinyuchan/Desktop/TKUXPython/Data/Aboard.csv',encoding='big5')
Aboard.head()
| 首站抵達地 | 細分 | 2002 | 2003 | 2004 | 2005 | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 亞洲地區 | 香港 Hong Kong | 2418872 | 1,869,069 | 2,559,705 | 2,807,027 | 2,993,317 | 3,030,971 | 2,851,170 | 2,261,001 | 2,308,633 | 2,156,760 | 2,021,212 | 2,038,732 | 2,018,129 | 2,008,153 | 1,902,647 |
| 1 | 亞洲地區 | 大陸 Mainland China | 1 | 44 | - | - | - | - | 188,744 | 1,516,087 | 2,424,242 | 2,846,572 | 3,139,055 | 3,072,327 | 3,267,238 | 3,403,920 | 3,685,477 |
| 2 | 亞洲地區 | 日本 Japan | 797460 | 731,330 | 1,051,954 | 1,180,406 | 1,214,058 | 1,280,853 | 1,309,847 | 1,113,857 | 1,377,957 | 1,136,394 | 1,560,300 | 2,346,007 | 2,971,846 | 3,797,879 | 4,295,240 |
| 3 | 亞洲地區 | 韓國 Korea,Republic of | 120208 | 179,893 | 298,325 | 368,206 | 396,705 | 457,095 | 363,122 | 388,806 | 406,290 | 423,266 | 532,729 | 518,528 | 626,694 | 500,100 | 808,420 |
| 4 | 亞洲地區 | 新加坡 Singapore | 190455 | 125,491 | 160,088 | 184,926 | 204,834 | 189,835 | 167,479 | 137,348 | 166,126 | 207,808 | 241,893 | 297,588 | 283,925 | 318,516 | 319,915 |
Pandas¶
Reading Files¶
.read_excel( ): 讀取 excel 資料
100-104 年各縣市消防人力人數統計
source:內政部統計查詢網 http://statis.moi.gov.tw/micst/stmain.jsp?sys=100
Fire = pd.read_excel('/Users/hsinyuchan/Desktop/TKUXPython/Data/Fire.xlsx')
Fire.head()
| 年度 | 區域 | 男 | 女 | 未滿25歲 | 25-29歲 | 30-34歲 | 35-39歲 | 40-44歲 | 45-49歲 | 50-54歲 | 55-59歲 | 60-64歲 | 65歲以上 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 100年 | 新北市 | 1833 | 244 | 263 | 880 | 540 | 163 | 93 | 89 | 29 | 15 | 5 | 0 |
| 1 | 100年 | 臺北市 | 1424 | 220 | 194 | 329 | 435 | 267 | 132 | 166 | 93 | 19 | 8 | 1 |
| 2 | 100年 | 桃園市 | 905 | 110 | 199 | 311 | 211 | 107 | 73 | 80 | 28 | 4 | 2 | 0 |
| 3 | 100年 | 臺中市 | 974 | 117 | 136 | 266 | 220 | 136 | 116 | 145 | 59 | 12 | 1 | 0 |
| 4 | 100年 | 臺南市 | 841 | 78 | 20 | 145 | 230 | 165 | 119 | 156 | 73 | 9 | 2 | 0 |
Pandas¶
Reading Files¶
.read_json( ): 讀取 JSON 格式資料
臺北市施工資訊
source:台北市政府資料開放平台 http://data.taipei/opendata/datalist/datasetMeta?oid=4d29818c-a3ee-425d-b88a-22ac0c24c712
construction = pd.read_json('/Users/hsinyuchan/Desktop/TKUXPython/Data/construction.json')
construction.head(1)
| AC_NO | ADDR | APPMODE | APPTIME | APP_NAME | CB_DA | CE_DA | CO_TI | C_NAME | DELAYTIME | ... | ST_NO | TC_MA | TC_MA3 | TC_MA3ID | TC_MAID | TC_NA | TC_TL | TC_TL3 | X | Y | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 102004900 | 紹興南街17~21-3號與仁愛路1段1~19號 | 0 | 1061121091240 | 台電輸變電 | 1020708 | 1061225 | 依交維計畫訂定時間施工 2月11日-3月2日禁止道路施工 | 中正 | NaN | ... | 1 | 黃少榮 | 連彥宇 | F126173460 | G121445426 | 長聖營造有限公司 | 988038303 | 937141297 | 302673.265 | 2770188.888 |
1 rows × 23 columns
import codecs
construction = pd.read_json(codecs.open('/Users/hsinyuchan/Desktop/TKUXPython/Data/construction.json', 'r', 'utf-8'))
Temperature_dataframe
| Kaohsiung | Quality | Taipei | |
|---|---|---|---|
| FEB | 21.1 | Good | 17.0 |
| JAN | 21.7 | Good | 8.3 |
| MAR | 22.9 | Bad | 20.1 |
| APR | 25.7 | Bad | 22.6 |
| MAY | 28.4 | Bad | 27.0 |
| JUN | 28.4 | Good | 27.8 |
| JUL | 29.4 | Bad | 30.1 |
| AUG | 30.2 | Bad | 30.3 |
| SEP | 29.7 | Good | 29.4 |
| OCT | 28.9 | Bad | 27.1 |
| NOV | 26.9 | Good | 24.0 |
| DEC | 21.6 | Good | 17.5 |
Exercise 查看 Temperature_dataframe 的前五筆資料
Temperature_dataframe.head(5)
| Kaohsiung | Quality | Taipei | |
|---|---|---|---|
| FEB | 21.1 | Good | 17.0 |
| JAN | 21.7 | Good | 8.3 |
| MAR | 22.9 | Bad | 20.1 |
| APR | 25.7 | Bad | 22.6 |
| MAY | 28.4 | Bad | 27.0 |
Exercise 查看 Temperature_dataframe2 的後三筆資料
Temperature_dataframe.tail(3)
| Kaohsiung | Quality | Taipei | |
|---|---|---|---|
| OCT | 28.9 | Bad | 27.1 |
| NOV | 26.9 | Good | 24.0 |
| DEC | 21.6 | Good | 17.5 |
Exercise 確認 Temperature_dataframe 的欄位資料類型
Temperature_dataframe.info()
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'> Index: 12 entries, FEB to DEC Data columns (total 3 columns): Kaohsiung 12 non-null float64 Quality 12 non-null object Taipei 12 non-null float64 dtypes: float64(2), object(1) memory usage: 384.0+ bytes
Exercise 查看 Temperature_dataframe 中連續型資料的基本統計敘述
Temperature_dataframe.describe()
| Kaohsiung | Taipei | |
|---|---|---|
| count | 12.000000 | 12.000000 |
| mean | 26.241667 | 23.433333 |
| std | 3.496611 | 6.675373 |
| min | 21.100000 | 8.300000 |
| 25% | 22.600000 | 19.450000 |
| 50% | 27.650000 | 25.500000 |
| 75% | 29.025000 | 28.200000 |
| max | 30.200000 | 30.300000 |
Exercise 查看 Temperature_dataframe 中類別型資料的次數
Temperature_dataframe['Quality'].value_counts()
Bad 6 Good 6 Name: Quality, dtype: int64
Matplotlib¶
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
Year = ['2014','2014','2014','2014','2014','2014','2014','2014','2014','2014','2014','2014',
'2015','2015','2015','2015','2015','2015','2015','2015','2015','2015','2015','2015',
'2016','2016','2016','2016','2016','2016','2016','2016','2016','2016','2016','2016']
Month = ['JAN','FEB','MAR','APR','MAY','JUN','JUL','AUG','SEP','OCT','NOV','DEC',
'JAN','FEB','MAR','APR','MAY','JUN','JUL','AUG','SEP','OCT','NOV','DEC',
'JAN','FEB','MAR','APR','MAY','JUN','JUL','AUG','SEP','OCT','NOV','DEC']
Season = ['Winter','Winter','Spring','Spring','Spring','Summer','Summer','Summer','Fall','Fall','Fall','Winter',
'Winter','Winter','Spring','Spring','Spring','Summer','Summer','Summer','Fall','Fall','Fall','Winter',
'Winter','Winter','Spring','Spring','Spring','Summer','Summer','Summer','Fall','Fall','Fall','Winter']
Taipei = [16.8,16.5,18.9,22.5,25.2,28.0,30.5,30.2,29.7,24.7,22.3,16.5,
16.7,20.8,18.9,22.7,26.1,30.0,30.0,28.6,27.4,25.2,23.5,18.9,
16.2,15.5,17.5,24.0,27.1,29.4,30.3,30.1,27.8,27.0,22.6,20.1]
Taichung = [16.4,17.0,19.8,24.1,25.8,28.6,30.1,28.9,29.2,25.6,23.1,17.1,
17.1,18.1,20.7,24.4,26.9,29.7,29.2,28.0,27.8,26.2,24.3,19.6,
16.8,16.4,18.3,24.9,27.6,28.8,29.4,28.9,27.9,27.5,23.4,20.4]
Kaohsiung = [19.5,20.3,22.6,25.9,27.8,29.2,30.3,29.1,29.5,27.2,25.2,20.2,
19.9,17.3,23.6,26.2,28.3,30.6,29.5,28.8,28.8,27.7,26.2,22.4,
19.3,19.6,21.6,26.9,28.9,29.7,30.2,29.4,28.4,28.4,25.7,22.9]
Temperature_table = { "Year" : Year,
"Month" : Month,
"Season" : Season,
"Taipei" : Taipei,
"Taichung" : Taichung,
"Kaohsiung" : Kaohsiung }
Temperature = pd.DataFrame(Temperature_table)
print(Temperature.shape)
Temperature.head()
(36, 6)
| Kaohsiung | Month | Season | Taichung | Taipei | Year | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 19.5 | JAN | Winter | 16.4 | 16.8 | 2014 |
| 1 | 20.3 | FEB | Winter | 17.0 | 16.5 | 2014 |
| 2 | 22.6 | MAR | Spring | 19.8 | 18.9 | 2014 |
| 3 | 25.9 | APR | Spring | 24.1 | 22.5 | 2014 |
| 4 | 27.8 | MAY | Spring | 25.8 | 25.2 | 2014 |
Taipei_Season = Temperature['Taipei'].groupby(Temperature['Season']).mean()
Taipei_Season
Season Fall 25.577778 Spring 22.544444 Summer 29.677778 Winter 17.555556 Name: Taipei, dtype: float64
Exercise 想知道 Temperature 資料中 台北市 及 台中市 溫度的關係
plt.scatter(Temperature['Taipei'], Temperature['Taichung'])
plt.show()
Exercise 想知道 Temperature 資料中 台北市 及 台中市 溫度的關係,加入標籤及標題
x = Temperature['Taipei']
y = Temperature['Taichung']
plt.scatter(x, y)
plt.xlabel("Taipei")
plt.ylabel("Taichung")
plt.title("Taipei VS Taichung")
plt.show()
x = np.arange(-2.0, 2.0, 0.01)
y = np.sin(2 * np.pi * x)
plt.plot(x, y)
plt.xlabel("x")
plt.ylabel("y")
plt.title("f(x) = sin(x)")
plt.show()
Exercise¶
Q. Line Plot¶
$$ f(x) = x^2 ; -2 \le x \le 2 $$
Answers¶
x = np.arange(-2.0, 2.0, 0.01)
y = x**2
plt.plot(x, y)
plt.xlabel("x")
plt.ylabel("y")
plt.title("$f(x) = x^2$")
plt.grid(True)
plt.show()
normal_data = np.random.normal(size = 10000)
plt.hist(normal_data)
plt.title("Normal distribution")
plt.show()
uniform_data = np.random.uniform(size = 10000)
plt.hist(uniform_data)
plt.title("Uniform distribution")
plt.show()
normal_data = np.random.normal(size = 10000)
uniform_data = np.random.uniform(size = 10000)
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.hist(normal_data)
plt.title("Normal distribution")
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.hist(uniform_data)
plt.title("Uniform distribution")
plt.show()
Exercise 利用 Taipei_Season 畫一個,台北在不同季節下的溫度變化
season_cut = range(len(Taipei_Season))
plt.bar(season_cut , Taipei_Season, color="blue", align = "center")
plt.xticks(season_cut , Taipei_Season.index)
plt.show()
 source:
source: source:
source: